
The new recast of the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) calls for all new buildings to be nearly zero energy buildings by the end of 2020. If all buildings implemented various energy-efficiency measures, electric bills would be 10 per cent lower by 2035. Energy efficiency of buildings is one of the basic requirements of current architectural engineering. If a building has the ability to require low energy to provide comfort, the size of the solar PV system able to cover its demand would be much. These advanced options, which are the primary focus of this roadmap, are needed not only to support whole-building approaches but also to improve the energy efficiency of individual components. An effective building envelope will lower the cost of fuels and power that control interior climates, and will improve the level of comfort as well as the health and safety of tenants within the building. This study proves that energy efficiency in homes is possible, by installing high performance building envelope materials, and can be an effective strategy to reach the concept of low energy buildings. That is why we are striving to achieve the most stringent energy efficient building standard in existence today the Passive House standard. While whole-building approaches are ideal, every day building envelope components are upgraded or replaced using technologies that are less efficient than the best options available. Informing Energy-efficient Building Envelope Design Decisions for Hong Kong.pdf.

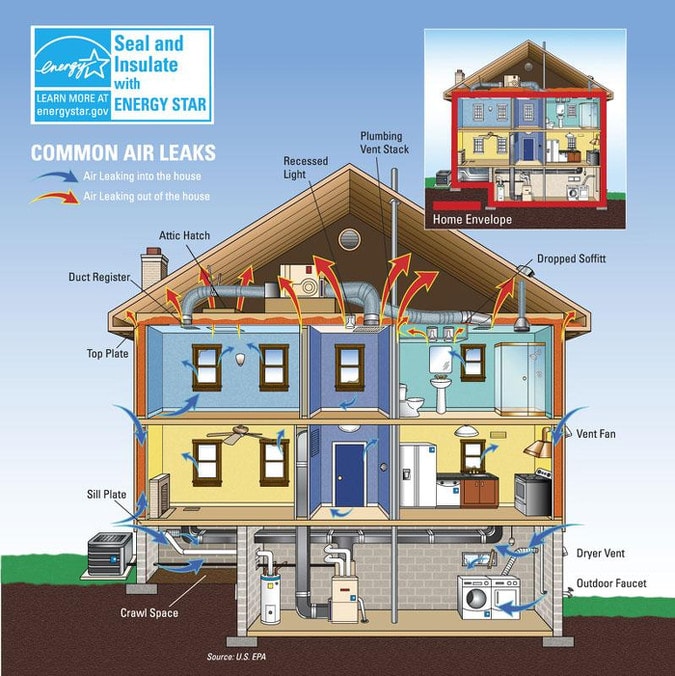
Overall, buildings are responsible for more than one-third of global energy consumption. The building envelopes impact on energy consumption should not be underestimated: globally, space heating and cooling account for over one-third of all energy. The building envelope’s impact on energy consumption should not be underestimated: globally, space heating and cooling account for over one-third of all energy consumed in buildings, rising to as much as 50% in cold climates and over 60% in the residential sub-sector in cold climate countries. The Envelope Showcase takes a deep dive into the building envelope, detailing system principles.
Energy efficient building envelope series#
The energy performance of building envelope components, including external walls, floors, roofs, ceilings, windows and doors, is critical in determining how much energy is required for heating and cooling. The membrane merely forms the outer envelope of a multipleshell roof construction the inner roof is flat, thermally insulated and only partly translucent. Building Energy Exchange is proud to announce the official launch of our Envelope Showcase, the first in a series of rotating showcases that expand upon the core building systems outlined in our 2020 Anatomy of an Energy Efficient Building exhibit. The building envelope – also known as the building shell, fabric or enclosure – is the boundary between the conditioned interior of a building and the outdoors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
